How to identify a virus masquerading as the svchost system process. How to identify a virus masquerading as the svchost system process. You need the svchost exe process.
Computer users want their machines to work as quickly as possible and not slow down. In search of “brakes,” they turn to the task manager to detect resource-intensive processes and unload them from memory. Often svchost.exe is visible in the list of processes. This program runs in many copies, and consumes a lot of RAM.
The natural question is: is it a virus or other malicious software if it overloads the computer like this? And another question: is it possible to delete svchost.exe and do without it. Usually the answer is negative to both questions: it is not a virus and it is almost impossible to do without it. But first things first…
svchost.exe is a system process in Windows starting from version 2000. This is the main process that helps run dynamic library services. If you delete the svchost.exe file, the computer will work... only several times slower than usual. The situation is not so paradoxical: although the system service takes up a lot of RAM, without it the ROM load would only be higher. The CPU load will also be high.
svchost.exe virus
But still, sometimes it is necessary to delete svchost.exe. More precisely, not himself, but viruses and Trojan horses masquerading as this application. It is easy to distinguish them: although the original system process also creates many copies, the malware is located in any directory except the system one.
It is also useful to know that you can see such a program in the task manager if you pay attention to running it as a user. In some cases, viruses use a genuine system service to cause damage.
There is no need to raise an alarm and worry about the fact that svchost.exe runs in ten copies. There are many dynamic services in the system; one process may not be enough for all of them. Then several copies are turned on at once, each with its own identifier. But we must also look at its origin carefully.
The real process runs from the folders: ServicePackFiles\i386, system32, Prefetch, winsxs\ (all inside C:\WINDOWS). If you notice that svchost.exe was launched from somewhere else, then this is a bad sign (as is the situation with a name that differs “just a little” from the original).
In such cases, run a full antivirus scan until you get rid of the malware.
Today we will talk about Svchost.exe, what kind of process it is and why it can load the system.
How to access the processes tab
While the computer is working normally, the average user is of little interest in what processes are running in the system and what they are needed for in general.
But the non-standard behavior of Windows XP/Vista/7 - slowdowns, freezing, frequent reboots - forces us to look for reasons.
Where to start your search? Let's try to launch the "Task Manager".
Launch options.
- Press the key combination “Ctrl” + “Alt” + “Del”.
- Click the “Start” button, select the “Run” command, enter taskmgr.exe and click the “Ok” button.
Now go to the “Processes” tab and study the list.
A large number of svchost.exe processes is immediately alarming. Well, it's time to understand the capabilities of this application.
First acquaintance with svchost.exe
Recently, instead of the usual executable files with the .exe extension, dynamic link libraries with the .dll extension are increasingly being used to compose Windows services.
This method is considered more effective. However, a library file, unlike an executable one, cannot start on its own.
The svchost.exe application “helps” to start a service from a dll file.
For example, here's how the DNS Client service starts:
C:\WINDOWS\system32\svchost.exe -k NetworkService.
A few words about svchost.exe processes
Each instance of the svhost.exe process is initiated by its parent, the services.exe system process.
A single svshost.exe process can run one service or a group of several logically related Windows services.
The launch option “one svchost process -> several Windows services” allows you to save RAM and processor resources.
To view svchost groups and their composition, go to the Windows registry:
- Click the “Start” button and find the “Run” command;
- In the command line, enter regedit.exe and click the “Ok” button.
- in the registry go to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Svchost branch;
- we find the REG_MULTI_SZ parameters with lists of services for each group.

For example, the DcomLaunch group includes the following services:
- Power – a service that manages power configuration and sends notifications about installed power configurations;
- PlugPlay is a service through which the computer automatically recognizes devices connected to it and configures them to work without user interaction or minimize this participation.
- DcomLaunch is a service for launching COM and DCOM servers for stable operation of programs using server data.
It is not recommended to disable any of the above services.
When viewing the svchost process data, be sure to pay attention to the Username column.
It can only contain one of the following values: “Local Service”, “System”, “Network Service”.

Where does the file live?
In Windows XP/Vista/7 operating systems, the location of the svchost.exe file is standard:
- 32-bit OS – C:\Windows\System32\;
- 64-bit OS – C:\Windows\SysWOW64\.

Let's remember the exact address of the file. This will be useful to us later.
The svchost.exe process and its connections
The task manager gives us a whole list of running svchost.exe processes, but this information is clearly not enough.
Naturally, we are interested in which services are launched by a specific instance of this process.
So, here are a few ways to find out about svchost's connections.
Tasklist and sc commands.
The tasklist and sc commands can be used in any version of Windows. Therefore, this method can be considered universal.
First of all, launch cmd – the Windows command line interpreter:
- press the “Start” button;
- select the “Run” command;
- enter cmd and press the “Ok” button.
To get a list of services on the interpreter screen, run the tasklist command with the svc key and press the “Enter” key:
- tasklist /svc "Enter".

To save the query results to the text file svc.txt located on drive C: in the temp folder, we redirect the output of the tasklist command:
- tasklist /svc > C:\temp\svc.txt “Enter”

Note that the file will be saved in DOS encoding.
Fragment of listing tasklist.exe.
Service PID Image Name:
- svchost.exe 1216 DcomLaunch
- svchost.exe 1300 RpcSs
- svchost.exe 1384 WudfSvc
- svchost.exe 1528 Dnscache
- svchost.exe 1584 LmHosts, SSDPSRV
Table columns:
- “Image name” – the name of the executable file;
- “PID” – process identifier;
- “Services” – list of services.
To obtain information about a specific service, set its short name as a parameter of the sc service management command.
An example of obtaining information about the TermService service.
– sc qc TermService “Enter”.
Two ways to get to the list of services.
- Click the “Start” button, find the “Run” command, enter services.msc in the command line and click the “Ok” button.
- Click the “Start” button, then select Settings -> Control Panel -> Administrative Tools -> Services.

Windows Vista/7 Task Manager.
We get a list of services associated with the svchost process using the Windows Vista/7 task manager:
- place the cursor on the process name;
- Call the context menu by right-clicking and select the “Go to services” option;
- We get a list in which the services associated with our process are highlighted.

In the Windows XP operating system, the “Go to Services” option, unfortunately, is missing. This option cannot be considered universal.
Process Explorer utility.
This program is not included in Windows distributions, but is available for download from the Microsoft website or from the Process Explorer download page.
The launch process is very simple and does not require installation:
- download the zip archive;
- run the file procexp.exe.
The utility provides detailed information about the processes running in the system: pid, cpu load, brief description, information about the manufacturer, etc.
When we hovered the mouse over the name of one of the svchost instances, we received the following information:
- Command Line – line for launching a service or group of services via svchost;
- Path – path to the svchost.exe file;
- Services – list of services.

The right-click context menu provides greater control over the process and the services it runs.
AnVir Task Manager utility.
The AnVir Task Manager program not only provides management of running processes, services, drivers and startup, but also performs antivirus functions.
The startup procedure is the same as for Process Explorer:
- download the free version of AnVir Task Manager in zip archive format;
- unzip to a folder on disk;
- run the AnVir.exe file.

To switch the language when you first start the program, use the main menu:
"View->Language->Russian".
Select the “Processes” tab to get detailed information about our svchosts.
In the process line we see information about the manufacturer, the path to the executable file, the CPU load percentage, etc.
But the most interesting data is presented in the “Startup” column. Here you will find a list of services launched by svchost.
Double-click the left mouse button on the process name and get more detailed information about it (a window with tabs at the bottom of the screen).
The system is slow, what should I do?
What symptoms indicate the culprit of svchost and how to fix the problem. Let's figure it out.
The system may slow down for various reasons. But if in the task manager you find the svchost.exe process with a high percentage of CPU load (sometimes even about 100%), it is likely that this is the reason.

Many users believe that in this case svchost is definitely a virus. But that's not true. A process can load the system for other reasons.
Let's look at how to solve the problem with svchost in both cases.
Is Svchost a virus or not?
Many Trojans and other computer viruses disguise themselves as well-known Windows system applications. Svchost is no exception.
According to Kaspersky Lab, the Trojan-Clicker.Win32.Delf.cn, Virus.Win32.Hidrag.d, Net-Worm.Win32.Welchia.a viruses, as well as the Kido virus known to most users, “pretend” to be svchost.
So, let's start checking our process.
First of all, pay attention to. If it differs from the standard one, you can safely delete the file.
Check the username that started the process. A list of valid names is given in the "" section.
Carefully re-read the process name. Virus writers often use similar names: svhost, svchosts, etc.
An application can never be launched through the "Run" key of the Windows registry.
Therefore, you definitely need to check its presence in startup:
- click the “Start” button, select the “Run” command, enter msconfig and click the “Ok” button;
- if the svchost.exe file is found, disable the launch.

To delete a suspicious process in the task manager, call up the context menu by right-clicking and select the “End process tree” command.
After completing all the described steps, you must run an anti-virus program and disinfect your computer.
How to remove the svchost.exe virus? Virus infection of the SVCHOST.EXE process is a very common occurrence. This is due to the fact that Windows uses svchost.exe processes simultaneously for different purposes. Therefore, it is beneficial for the virus to get lost among them and act like a resident. Symptoms usually include heavy or full computer loading. The network and internet stop working. If there are many suspicious svchost.exe processes in the task manager, this does not mean that you have a virus.
Windows uses this process for many things, such as updating the OS. A sign that raises suspicion of the presence of a virus is an active svchost.exe process launched by the user. If you see this process running not from NETWORK SERVICE, LOCAL SERVICE or SYSTEM, but from your account, then there is probably a Trojan on the computer.
Unfortunately, the actions of such viruses sometimes lead to severe damage to the system. This problem can be solved in two ways. Either full or by restoring the registry. We will describe simple recommendations that will answer the question “How to remove a Trojan virus from svchost.exe?” Note that before scanning with an antivirus, you need to disconnect from the Internet and local network, that is, unplug the cable from the network card. Connect the USB drives you use.
- So, the first thing we can recommend is to install a good antivirus. Not all virus removal programs are suitable for scanning. But there are several software solutions that should help in the fight against the virus embedded in SVCHOST.EXE.
- Disable the System Restore service (relevant for Windows XP). It's done like this. Right-click on My Computer -> Properties -> System Restore tab -> check the box Disable system restore on all drives. This is done so that the svchost.exe virus does not return after treatment.
- Check startup. Click Start -> Run (for Win 7 the command line is immediately available) -> enter “msconfig”. It should not contain svchost.exe files.

- Download CureIT – http://www.freedrweb.com/cureit and check all logical drives and flash drives in Windows safe mode.
In principle, you don’t have to download CureIT and use a high-quality antivirus with updated signatures, but it’s better to play it safe and check everything in two different ways. After checking, you may need to restore the Windows registry keys. If something doesn’t work out, you can always call and order a virus removal service. And for those who find these recommendations insufficient, we advise you to read the article about that - it shows a detailed method for removing viruses manually.
Question from a user
Good afternoon.
I have Windows 7 installed on my computer, and lately it has started to slow down. Empirically, I found that the “svchost.exe” process loads the 2-core processor 50%-100% (at least that’s what it shows in the task manager).
I tried to end this process, but an error appears and the computer goes into reboot. Is it possible to complete it at all, and how can I reduce the load from it? In general, what is it for and why does it load the system so much?
Thank you in advance.
Dmitry, Arkhangelsk
Good day.
All popular versions of Windows (XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10) have this special process svchost.exe (note: its full name is Generic Host Process for Win32 Services).
It is used as a platform for the operation of various services (i.e., a purely systemic process that is not advisable to “touch” if everything is working normally for you).
If you open task manager, you will see that there are several lines with svchost.exe (which is not surprising, since Windows always runs many services and applications: Windows Defender, OS update, font service, etc.). And this process loads the CPU, most often due to some service that has started not working correctly.
In addition, it is also worth noting that many viruses are disguised as this system process: after all, if there are many of them, then determine which one of them is not real- not so easy for an untrained user.
And so, let's consider below what can be done if svchost.exe loads the system...
Solving the problem with svchost.exe
Of course, the advice is banal, but still, a seemingly simple reboot of the computer helps solve many problems (including this one 👌). N
Often, when connecting/disconnecting peripheral equipment, or when services or drivers malfunction, svchost.exe begins to create an excessive load, which “disappears” after the PC is rebooted. So let's try it!
👉 Isn’t it a virus masquerading as svchost.exe? Let's check!
As I noted just above in the article, many viruses often disguise themselves as this system process. Distinguish the real process svchost.exe from a virus is not always easy! 👀
But we will deal with this now (it is very advisable to first exclude viral activity, and if the high load was not associated with this, then move on to solving problems with services).
To begin, open the Windows Task Manager (buttons Ctrl+Shift+Esc or Ctrl+Alt+Del).
Then open the tab "Processes", sort them by name and look carefully: what is written next to each svchost.exe in the column "User" (screenshot below to help 👇).

Task Manager (Windows 7) - View Processes
👉 I want it right away It should be noted that it is not always possible to “see” all processes in the task manager, and it is not always possible to discern which of them is “not real”. In general, it is much more effective to use a special one for this purpose 👉 (I have praised her more than once in my articles...).
By launching the AVZ utility (by the way, you don’t need to install it), open the menu "Service" and open "Process Manager" .
Then also sort processes by name and find all svchost.exe. Please note that the utility shows ALL processes (that's why there are so many of them).
👉 Important!
Everyone is normal svchost.exe AVZ is marked in green. Moreover, in the column "Description" it will be indicated that this is “Host process...”, “Manufacturer” - “Microsoft Corporation...”, “Full path” - “C:\Windows\System32\svchost32.exe”.

If you find something suspicious, try closing this process, and then scan your computer completely with the AVZ utility for viruses and Trojans. This is done quite simply:

👉 To help!
The best antiviruses to protect Windows -
👉 Which service loads the service host?
And so, the computer has been checked, there are no viruses, let's move on...
Open the task manager again (Ctrl+Shift+Esc buttons) and look for that svchost.exe, which loads the processor. Once you find it, right-click on it and open the link "Go to Services" (see screenshot below 👇).

This will show you ALL services associated with the svchost process that is consuming the CPU.
Now close these services one by one, looking at the load on the processor. As soon as she falls- you have found the service that is to blame for the load!
👉 Important!
In the process of closing some services, your Windows may reboot. Therefore, it is better to remember what you have already tried to close (so that next time you can close other services associated with this process).

When a service is found that is causing high load - what to do?
This is a common and rather difficult question. The fact is that there are quite a lot of services that can cause a high load. Giving universal advice (or providing all possible options) is unrealistic!
If the failure is caused by a minor service that you can easily do without, simply disable it (for example, the Superfetch service is often a stumbling block).
If you really need the service (for example, it is associated with audio and video equipment, network adapters, etc.)- then try replacing the driver with the hardware (update or vice versa, install an older one).
👉 Disable the update center, Superfetch (and other services)
Very often the culprits of high file load svchost are services "Update centre" And "Superfetch" (therefore, in case of this problem, I recommend disabling them, at least for a while for testing).
To disable them, you need to open the tab "Services" .
How to open services (universal method):
- press the Win+R button combination;
- enter the command services.msc and press Enter.

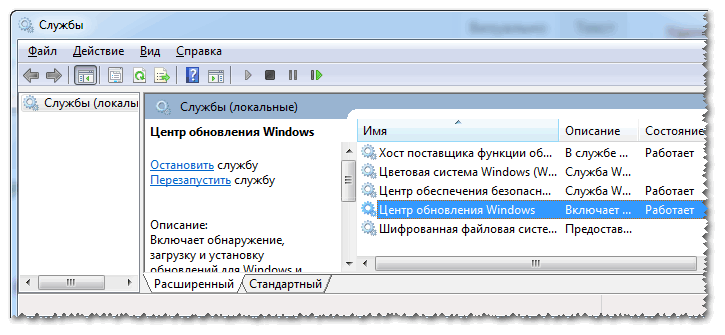
In the column "Startup type" put "Disabled", and in the block "State" click the button "Stop" .
All! The service is now disabled and will no longer start!

👉 Important!
Be careful and don't turn off everything. In some cases, users got so carried away with disabling services that they were then unable to restore their Windows functionality.
❺
👉 Roll back the system a few days/weeks ago
If a high load on the processor appeared not so long ago, and there are recovery checkpoints, then you can try to run Windows recovery and roll it back to a working state.
Despite the fact that many users underestimate this method, it is very effective and helps solve many problems.
How to run System Restore:

👉 To help!
For more information about restoring Windows (and analysis of all typical questions), you can
❻
👉 Removing the Prefetch folder
There is another way that helps some people solve the problem with svchost...
1) You need to find the Prefetch folder (note: on the system drive "C:\Windows") and delete it.
2) Then find the Tasks folder (located at this path "C:\Windows\System32"), open it and delete all files from it.
3) After this procedure, simply restart your computer.
Note: this method is controversial, use at your own risk.
How many "svchost.exe" processes should be running? It is impossible to answer this question, since in each case the number of running “svchost.exe” processes is different. This depends not only on the version of your operating system, but also on its build!
Since it is impossible to know the exact number of processes, the creators of the malware could not take advantage of this moment!
A huge number of viruses, Trojans and other malicious programs have chosen the “svchost.exe” process and, in order to disguise themselves in the system, disguise themselves as this process.
That is, malicious programs are launched with the name “svchost.exe” and are lost among many system processes with the same name. This leads to the fact that the chances of remaining undetected in the system increase several times.
How to identify the malicious process svchost.exe
Naturally, if the user suspects that the “svchost.exe” process is malicious, then the first thing the user will do is scan the computer for viruses and other things.
But, if after scanning the antivirus program reports that the system is clean and no malware was detected, this may not be entirely true!
In this case, it is worth checking the “svchost.exe” process manually. This is done quite simply, all you need is to know a few things about the svchost.exe process.
1) The process always runs from the system folder “System32.” If this is not the case, then most likely the file named svchost.exe is malicious.
2) The svchost.exe process will never run as the user - this must be remembered. The process always starts from “Local Service, System, Network Service”.
As you understand, if the svchost.exe process was launched under the current user name or not from the system folder, then it is worth taking measures to check the suspicious file.
To make sure that the original file is running, launch the task manager and look in the “Details” tab for the list of “svchost.exe” processes.
In this screenshot, all processes are launched by the system itself, which means that most likely there is no malicious file named “svchost.exe” in this list. Pay attention to the screenshot below...
In this screenshot we see the svchost.exe process running from a user named “SuperUser”. This suggests that this process is more malicious.
You need to press “RMB” and select “Open location” from the context menu. Windows Explorer will open and you will find out the full path to the suspicious file! What to do with him next, I think it’s clear as day!
Important to know: Some viruses simply use the name “svchost.exe” to hide their presence in the system, but they can also use the original svchost.exe file for their own selfish purposes.
In this regard, a manual check will not give results here! It was also already said above that an antivirus may not give any results in searching for a virus! A logical question arises: what to do?
As an option, use a free “firewall”, among which I personally highlight “comodo firewall”, how can it help us? It's simple! If a virus using the svchost.exe process suddenly decides to show network activity, the user will be aware of this!
From the screenshot you can clearly see that the svchost file is trying to connect to the server on port 80, the original file will never do this, so svchost is infected!
You can quickly block network access for the svchost file, which would be quite reasonable! Since in this case, there is a possibility of transferring confidential data, such as passwords from the browser to the “Gate”
If such information leaks, you understand how it can end for you!
What to do with an infected svchost.exe file? Since the current antivirus and manual scanning are of absolutely zero use, open the website “virustotal.com” and check the file. By the way, do it right now!
My result is this. Everything is clean! If any antivirus would react, for example “Avast”, then I would uninstall the current antivirus and install Avast and cure svchost.exe.
