Opening CAP files. What is the CAP file extension? Why can't I open the CAP file?
A single network capture file (pcap format) can contain more than one handshake. This can happen, for example, when Airodump-ng is running for a long time, as a result of which it can intercept several handshakes from the same or different access points. Handshakes from files captured in “noisy” conditions need additional checking and cleaning.
Multiple handshakes in one file can be obtained artificially by simply combining them into one file. For example, the Besside-ng program (automatically captures handshakes from all access daughters within reach, for this it carries out a deauthentication attack) creates a single .cap file for all captured handshake packets.
Those. This is not an uncommon situation, and to carry out an attack on networks whose handshakes are in the same file, it may be necessary to extract each handshake.
How to split handshakes into different files
It's important to understand the difference between a file that's just a few handshakes stitched together and a file that's captured in a noisy environment. Example of analyzing a file of the first type (using aircrack-ng):
Aircrack-ng FILE_NAME.cap
Example of a file of the second type:
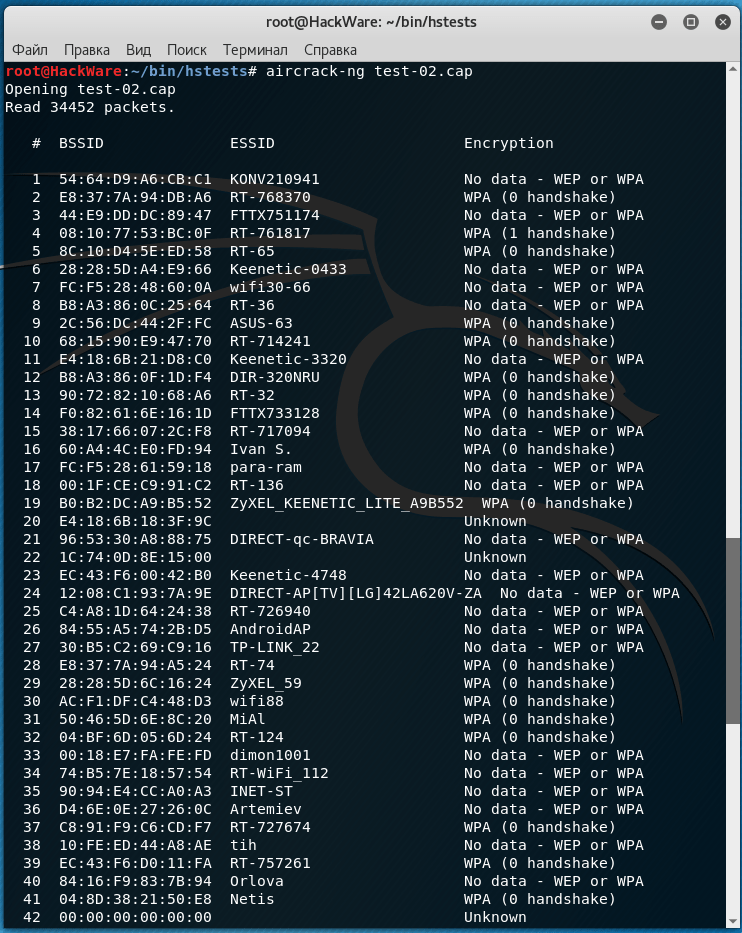
You can see that there is a lot of garbage in the second file, and there are only two hackable handshakes in the entire file. Among the garbage there are many individual EAPOL frames (components of a handshake) that are unsuitable for password guessing.
You can use Wireshark to view the contents of the file. After opening the file, set the filter:
Manually splitting handshake files using Wireshark
If you are working with a file of merged handshakes, then there should be no particular problems with it. Open the file in Wireshark:

You can use a filter
Wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x08 || wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x05 || eapol
But it may not be necessary, since only the necessary packages are already available.
To filter packets for a specific access point, specify it BSSID with the following filter:
Wlan.addr==BSSID
For example:
Wlan.addr==28:28:5D:6C:16:24
Or like this:
(wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x08 || wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x05 || eapol) && wlan.addr==28:28:5D:6C:16:24
Now with the help CTRL+m select the required packages:
And on the menu File select Export Specific Packets:

Enter a file name and check the radio button Marked packets only:

Let's check our file:

Everything is fine. You can do another check using coWPAtty by running a command like:
Cowpatty -r FILE -s NETWORK_NAME -c
For example, in my case:
Cowpatty -r ZyXEL_59.pcap -s ZyXEL_59 -c
Phrase " Collected all necessary data to mount crack against WPA2/PSK passphrase" means that all the necessary data to crack the password has been collected.
It takes some effort to extract a handshake from a grip performed in a noisy environment. Let's start with filtering (replace 84:C9:B2:52:F6:37 with BSSID network you are interested in):
(wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x08 || wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x05 || eapol) && wlan.addr==84:C9:B2:52:F6:37
Handshake is suitable for password cracking if:
- necessarily includes the second element (M2) as well as the third (M3) (guarantees that a connection to the network has been made) or instead of the third element contains the first element (M1) (the handshake is suitable for password cracking, but there is no guarantee that it has been made connection and that the correct password was entered). It is better if you managed to capture all four elements;
- the elements of a handshake must follow in the correct order;
- there should not be too much time between them (measured in milliseconds and microseconds).
Let's look at the following example.

The first set of EAPOL frames (highlighted in black) - the rule that there must be a third or first message in addition to the second is not followed.
The second set (red) - only one message.
Third set (yellow) - there is no third or first message.
Fourth set (orange) - no second message.
The fifth set (green) is suitable because there is a second and a first message. The time between messages seems acceptable.
Select and save the necessary frames (I also selected the Beacon frame):

Our file passes the checks:

Isolating a handshake using tshark
tshark is Wireshark, but without the GUI. This program can also be used to split a large capture file into individual handshakes. To do this, the command is run as follows:
Tshark -r SOURCE_FILE.cap -R "(wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x08 || wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x05 || eapol) && wlan.addr == BSSID" -2 -w FINAL_FILE.cap -F pcap
In it you need to insert your values for:
- SOURCE_FILE.cap- file with several handshakes
- BSSID- MAC address of the access point of interest
- FINAL_FILE.cap- file where the selected handshake will be saved
Example of a real command:
Tshark -r wpa.cap -R "(wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x08 || wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x05 || eapol) && wlan.addr == 84:C9:B2:0B:79:94" -2 -w $ESSID.cap -F pcap -w wifi55.cap
Solving the Unsupported file format (not a pcap or IVs file) error. Read 0 packets. No networks found, exiting.
For some users, when using tshark and then subsequently opening the resulting file in aircrack-ng an error occurs:
Aircrack-ng MiAl.cap Opening MiAl.cap Unsupported file format (not a pcap or IVs file). Read 0 packets. No networks found, exiting. Quitting aircrack-ng...
To avoid this error, when saving with the tshark program, you need to specify the option -F pcap, which specifies the correct file format.
Script for splitting handshakes
To automate the splitting of one file into handshakes, I wrote a script. Remember that if you split a file obtained using Beside-ng or artificially when merging handshakes, the script will work without problems.
If you are splitting a capture file acquired in noisy conditions (for example, during long periods of work) into separate handshakes Airodump-ng), then the script will work like this:
- if no working handshake is found for any access point, then all data for it will be discarded (no output file will be created)
- If at least one working handshake is found for the access point, then all EAPOL frames will be saved into one file.
Those. you will need to open the output files yourself and check if there is any unnecessary data in them.
Although aircrack-ng seems to correctly find the required handshake, problems have been noticed with cap2hccapx (from the hashcat-utils set, used to convert to the Hashcat hash format) if unnecessary EAPOL frames from unusable handshakes are not first cleared.
And copy there:
Expand
To run, specify the .(p)cap file from which you want to extract handshakes.
Example of the program:

If at least one working handshake is found, then a folder like 2018-04-13-155818 is created in the current directory, into which handshakes for all access points are saved as separate files.
Information about the file name with saved frames is displayed, as well as information about the saved frames themselves.
When you don't need to split a file into separate handshakes
You do not need to first split the file into separate handshakes if you are going to use the aircrack-ng program. To select a target you can use the following options:
E
Program cap2hccapx will write all hashes (for hacking in Hashcat) into one file.hccapx.
It starts like this:
Cap2hccapx.bin SOURCE_FILE.cap HASHES.hccapx
For example:
Cap2hccapx.bin wpa.cap all.hccapx

To record a hash for only one AP, specify it ESSID:
Cap2hccapx.bin SOURCE_FILE.cap HASHES.hccapx ESSID
Cap2hccapx.bin wpa.cap Zyxel-49.hccapx Zyxel-49
Size: px
Start showing from the page:
Transcript
1 CAP/CIPA Library. "Tasks and solutions." Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. Material downloaded from the site for personal use. Copying and commercial distribution is prohibited. For distribution inquiries please contact: All rights reserved CIPA Examination Network
2 Certified Public Accountant Mock Exam Management Accounting 1 Time Allowed: 4 hours Candidate ID: This exam contains five items, each with multiple parts. Complete all five tasks. Answer the questions on the Answer Sheet. Remember, any rough calculations and records should be kept on specially designated “For rough records” sheets. Entries made on “For rough records” sheets can be viewed when checking the work, however, solutions possibly contained in them will not be taken into account when accrual of points. At the end of the exam, turn in your Answer Sheet. In parentheses, after the name of each task, its maximum score is given. Recommended time allocation: Task 1, 18 points minutes Task 2, 10 points minutes Task 3, 11 points minutes Task 4, 11 points minutes Task 5, 50 points minutes Total time: minutes All monetary values are expressed in accounting units (cu. ), the international monetary unit used in this exam. Calculators are permitted. ATTENTION! The examination module must NOT be removed from the examination room. You must take this examination module along with your Answer Sheet. DO NOT GO TO THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU HAVE PERMISSION TO START THE EXAM. Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. 2
3 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in any data storage or retrieval system, or transmitted in any form by electronic or mechanical means, including photocopying, recording on any information storage or retrieval device, without prior permission CIPAEN Inc., except as expressly provided by law. CIPAEN Inc. Permit Requests should be sent to: Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. 3
4 Task 1 (18 points) A workshop for the production of ceramic products for landscape design uses the variable cost calculation method (direct costing system). The company uses a system of flexible budgets to analyze activities. The estimate for 2007 includes the following data: Sales volume of products at a price of 25.00 USD. for a unit; Costs per unit: Basic materials 1.6 kg at a price of 9 USD. per kilogram. The main labor is 0.5 hours, the tariff rate is 8.50 USD. in 1 hour. Variable overhead distribution factor 3.75 cu. for 1 hour of basic labor. Fixed overhead costs for the period c.u. Actual data for 2007: In fact, in 2007, products were produced and sold at a price of 26.50 USD. for a unit. During the year, kg of material was purchased and used at a cost of cu. The labor time spent by the main production workers on processing 1 unit amounted to 0.6 hours, the wages paid were c.u., and the wage arrears for 2007, according to the financial statements, amounted to c.u. In 2007, fixed overhead expenses were paid in the amount of c.u., of which c.u. This is insurance paid in advance for the next year. Actual variable overhead costs amounted to cu. Required: Answer the questions below. Enter your answers in a special form: Answer Sheet. For test questions, choose the best answer. Give only one answer to each question. Answer all questions. Your score will be based on the total number of correct answers. Consider that there is no connection between the questions and, unless otherwise specifically stated, the initial data is taken from the problem conditions. Round your answer to whole units according to the rules of mathematics (0.5 to 1) 1.1. What is the cost of production under a rigid budget? 1.2. What is the marginal income equal to under a rigid budget? 1.3. What is the income under a flexible budget? 1.4. What is the cost of production under a flexible budget? accounting 1. Trial exam. 4
5 1.7. Indicate what the deviation in the price of materials is equal to: a) cu, favorable b) cu, unfavorable c) cu, favorable d) cu, unfavorable 1.8. Indicate the correct formula for determining deviations in the use of materials a) standard price*(standard quantity for actual output, estimated quantity) b) standard price*(actually used quantity, standard quantity for actual output) c) actual price*(actually used quantity, standard quantity for actual output) d) actual price * (actually used quantity estimated quantity) 1.9. Indicate what the deviation at the labor rate is equal to a) 9000 cu, favorable b) 9000 cu, unfavorable c) cu, favorable d) 10800 , c.u. unfavorable Indicate what the deviation in labor productivity is equal to a) c.u., favorable b) c.u., unfavorable c) c.u., favorable d) c.u., unfavorable Indicate what the deviation for PNR variables is equal to efficiency a) 2700 c.u., favorable b) c.u., favorable c) c.u., unfavorable d) 16200 c.u., favorable 1.12. Deviation for PNR variables for use a) 2700 c.u., favorable b) cu, favorable c) cu, unfavorable d) CU 16,200, favorable The following information applies to questions 13 and 14. The company allocates fixed manufacturing overhead at a standard rate of CU 3.75. per 1 main labor (standard output units), actual commissioning and commissioning work are equal to cu. Indicate what the total deviation for constant commissioning and commissioning work is equal to a) 1000 cu., favorable b) 5,000 cu., unfavorable c) 7,500 cu. ., unfavorable d) 12500 c.u., unfavorable What is the deviation for constant commissioning and commissioning by volume a) 1000 c.u., favorable b) 5000 c.u., unfavorable c) 7500 c.u., unfavorable d) 12500 c.u. e., unfavorable Management Accounting 1. Trial exam. 5
6 Task 2 (10 points) Below is the Profit and Loss Statement of the Sever company for the 2007 financial year. In 2007, 80% of the design capacity of the Sever company was used. Profit and loss statement Company "Sever" 2007, USD Sales income (units at a price of 33 cu) Production costs: Basic materials Basic wages of workers Production overhead: Fixed Variable Gross profit Operating expenses (administrative and selling): Fixed Variables for sales Operating profit One of the company's managers developed a plan for the next financial year, involving the following changes: The company plans to reach full capacity and increase the price to 35 USD. for a unit. The effect of changes in prices for some types of materials will not be offset by an increase in the efficiency of their use, so the cost of raw materials and supplies will increase by 10% per unit of production. An increase in labor productivity with an increase in sales volumes will lead to an increase in tariff rates, so labor costs for key workers will increase by 16% per unit of production. Total fixed manufacturing overhead costs will increase by 7.14%. Total variable manufacturing overhead costs will increase in proportion to volume plus an amount equal to 15% of the increase in sales volume. Total sales costs will increase in proportion to the increase in sales volume, since additional costs will be required to increase sales volume. Administrative expenses will remain unchanged. Required: Answer the questions below. Enter your answers in a special form: Answer Sheet. For test questions, choose the best answer. Give only one answer to each question. Answer all questions. Your score will be based on the total number of correct answers. Consider that there is no connection between the questions and, unless otherwise specifically stated, the initial data is taken from the problem conditions. Round your answer to whole units according to the rules of mathematics (0.5 to 1) 2.1. Determine the company's break-even point in natural units 2.2. Determine the break-even point in monetary terms if the break-even point in natural units is equal to units. What is the safety margin equal to if the break-even point in natural units is equal to units? Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. 6
7 2.4. What is the planned output in natural units? 2.5. What are the planned direct costs per unit of production? 2.6. What are the planned production overhead costs per unit of production when using the absorption costing method, if the planned increase in sales volume is equal to c.u. What are the planned non-production costs equal to when sales volume increases by 30% 2.8. If the company's total expenses are described by the equation *X, where X is the number of products produced, then what is the break-even point in natural units 2.9. The plan proposed by one of the company's managers should be accepted a) if the break-even point does not change and the contribution margin increases b) if the break-even point decreases and the contribution margin increases c) if profit increases, regardless of how the break-even point changes d) if the contribution margin increases income and margin of safety Management Accounting 1. Mock exam. 7
8 Task 3 (11 points) The Region company produces three products - A, C, E - in two production departments - Department 1 and Department 2, each of which employs workers of two categories. You are an assistant cost accountant who is preparing annual estimates for 2007 and you have been assigned to prepare several calculations. You have the following information about the company's activities: Data Estimated inventories of finished products (in cu): Products A C E as of January 1, cu. 540 USD as of December 31st. 570 USD All inventories are valued at expected cost per unit (cu) Expected gross profit (defined as a percentage of selling price) Estimated sales volume (cu): % 25% 16.67% Northern region c.u. e.e. Southern region e.e.e.e. Western region 800 USD Total e.e.e.e. Expected labor time per unit and expected rates: Indicator Rate, Number of hours per unit. per hour product A product C product E Department 1 1st category 1.80 1.00 h 1.50 h 0.50 h 2nd category 1.60 1.25 h 1.00 h 0.75 h Department 2 1st category 2, 00 1.50 h 0.50 h 0.50 h 2nd category 1.80 1.00 h 0.75 h 1.25 h Management Accounting 1. Trial exam. 8
9 Required: Answer the questions below. Enter your answers in a special form: Answer Sheet. For test questions, choose the best answer. Give only one answer to each question. Answer all questions. Your score will be based on the total number of correct answers. Consider that there is no connection between the questions and, unless otherwise specifically stated, the initial data is taken from the problem conditions. Round the answer to whole units according to the rules of mathematics (0.5 to 1) 3.1. What is the selling price of each of products A, C, E 3.2. Let the selling price of product A be 30 USD. per unit, from 19 USD per unit, E 40 USD for a unit. What is the number of sold units of each product 3.3? Let the selling price of product A be 30 USD. per unit, from 19 USD per unit, E 40 USD for a unit. What are the inventories of each product at the end of the period? 3.4. It is known that product A product C product E Sales in units Inventories at the end of the period in units Inventories at the beginning of the period in units What quantity of products A, C, E must be planned for production 3.5. It is planned to produce 100 units. product A, 200 units. product C, 400 units. product E. What is the expected labor cost in department 1 for each product? 3.6. It is planned to release 100 units. product A, 200 units. product C, 400 units. product E. What is the expected labor cost in department 2 for each product? 3.7. It is planned to release 100 units. product A, 200 units. product C, 400 units. product E. The expected costs of basic materials and labor per unit are 14.5 cu. for product A, 7.5 USD for product C, 14.0 c.u. for product E. What is the company's expected manufacturing overhead? Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. 9
10 Task 4 (11 points) The Alberta company produces one type of product. The following information is available on the company's production activities for January 2008: Product units produced. Product units sold at a price of 30 USD. As of January 1, the volume of finished products was 20 units each. As of January 1, the volume of raw materials was kg at a price of 5 USD. for 1 kg. During January 2008, 2 purchases of raw materials were made: January 6, kg at a price of 6 USD. for 1 kg; January 22 kg at a price of 5 USD for 1 kg. Work in progress amounted to: January 1 units in the amount of cu; January 31 units for the amount of cu. Actual costs for January (in cu): Direct labor Indirect labor Sales salaries Administration salaries Product returns and discounts Advertising expenses Manufacturing utilities Rental of production facility Interest expense Other manufacturing overhead Allocated manufacturing overhead is 70% of total direct labor costs. Depreciation on fixed assets is calculated using the straight-line method at a rate of 10% per year. Assets at amortized cost: Production equipment cu; Production facilities c.e. The company uses the FIFO method to determine the cost of materials and finished products. To produce 1 unit, 1 kg of raw materials is required. The company's cost allocation policy stipulates that under- (over-) allocated costs of less than 5% are immaterial. Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. 10
11 Required: Answer the questions below. Enter your answers in a special form: Answer Sheet. For test questions, choose the best answer. Give only one answer to each question. Answer all questions. Your score will be based on the total number of correct answers. Consider that there is no connection between the questions and, unless otherwise specifically stated, the initial data is taken from the problem conditions. Round your answer to whole units according to the rules of mathematics (0.5 to 1) 4.1. What is the cost of materials used in January 2008? 4.2. Let the cost of materials written off as a debit to the work in progress account be c.u. What is the cost of manufactured products for January 2008? 4.3. What is the quantity of finished products as of January 31, 2008? What is the standard rate for the distribution of commissions equal to 4.5. If the actual commissions are equal to cu, then when using the standard rate, commissions a) are underdistributed to y .e. b) redistributed to USD c) underdistributed in monetary units. d) redistributed to USD 4.6.Indicate the amount of actual production overhead costs incurred for January 2008 a) c.u. b) c.u. c) c.u. d) c.e. What is the actual rate of distribution of the PNR, if the actual PPR is equal to the c.u. and direct labor costs 4.8 were selected as the distribution base. Indicate the amount of expenses for selling products a) c.u. b) c.u. c) c.u. d) cu If the cost of goods manufactured is, the amount. of actual commissioning and commissioning work, the amount of redistributed commissioning is equal to 2000 c.u., then what is the cost of goods sold reflected in the profit and loss statement? Management accounting 1. Trial exam. eleven
12 Task 5 (50 points) For each of the questions below, choose the best answer. Mark your answer on the answer sheet for all 25 questions. Give only one answer to each question. Answer all questions. Your score will be based on the total number of correct answers. 5.1 Which cost elements are considered direct production costs? Labor costs of managers Depreciation of production equipment a. yes yes b. yes no c. no yes d. no no 5.2 Basic production materials added in the second production workshop and not increasing production output: a. will increase the total unit cost of production; b. will not change the amount of costs transferred from this workshop; V. will reduce the balance of work in progress at the end of the period; d. will increase the amount of manufacturing overhead included in the ending work in process balance. 5.3 Which of the following statements regarding cost behavior is FALSE? for a. Fixed costs per unit change as production volume changes within the relevant area; b. Variable costs per unit are constant within the relevant area; V. Total variable costs are constant within the relevant area; d. Total fixed costs are constant within the relevant area. 5.4 The Company uses a predetermined overhead allocation method based on equipment operating hours. Factory general estimated overhead costs for the year are c.u., actual c.u. During the year the company distributed c.u. on the actual operating hours of the equipment. How many hours of equipment operation are included in the estimate? a hours; b hours; in hours; g. hours. no sales Management Accounting 1. Trial exam. 12
13 5.5 For the Saturn company, the following initial information is available for the past period: Estimated labor hours of the main employees Estimated overhead costs, cu Actual labor hours of the main employees Actual overhead costs, cu What is the planned rate of distribution of overhead costs per hour of labor of the main employees ? A. 34.40 USD in an hour; b. 35.00 USD in an hour; V. 36.88 USD in an hour; 37.52 USD per hour. 5.6 To fulfill a special order for the production of product X, the company purchased 10 tons of raw materials costing 3.00 USD. per kg. During a breakdown of the heating system in the warehouse, two tons of raw materials were flooded with water, completely spoiled and could not be used in the production of product X. 7 tons of raw materials were used in the production of product X, which was delivered to the customer. The customer paid for the products received, but asked the company to stop producing product X because he no longer needed it, and informed the company that the contract was being terminated. One ton of raw materials available in the company’s warehouse cannot be sold, since due to its specificity there is no demand for it. Which of the following costs is a sunk cost? a.u.; b.e.; in cu; g.e. 5.7 A manufacturing company has the following data on inventory at the beginning and end of the last reporting period (in cu): At the beginning of the period At the end of the period Raw materials and materials Work in progress Finished goods During the specified period, the company incurred the following expenses (in cu. ): Materials purchased Direct labor costs Indirect labor costs (production) Utilities and depreciation of the production building Salaries of sales and administrative personnel What is the cost of goods manufactured? a.u.; b.e.; in cu; g.e. Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. 13
14 5.8 If actual output is higher than budgeted, which of the following costs would be expected to be lower than budgeted? A. General variable costs; b. General fixed costs; V. Variable costs per unit of production; d. Fixed costs per unit of production. 5. Below is information on the production of three products A, B and C. Product A Product B Product C Sales cost at the cut-off point, thousand dollars Sales cost after further processing, thousand dollars Distributed complex costs, thousand dollars .e Added costs for further processing, thousand.e Which of the proposed options would be the correct decision to continue processing or sell? A. A is sold at the cutting point, and B and C are further processed; b. A and B are sold at the cutting point, and C is further processed; V. A, B, C undergo further processing; d. A, B, C sell at the point of division. 5.9 The Inter company has two divisions A and B, producing the same product. Product unit price - 20 USD Division A Division B Production costs 1 unit. products, cu: Direct costs for materials 5.2 5.2 Direct costs for wages 1.5 6 Variable overhead costs 5.3 5 Fixed costs At what volume of production will the costs of division A and division B be the same? a units; b units; in units; g units In the current period, Extra Company began producing units of product M. At the end of the period, units of product M were completed, and the remaining units were 30% complete. Determine the company's costs for each equivalent unit if costs in the amount of cu were incurred during the period. A. 1.84 USD; b. $2.40; V. 2.76 USD; g. 2.90 USD Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. 14
15 The following information relates to questions 12 and 13: In its first year of operation, Dream Company produced units. During the same period, units of production were sold at a price of 10 cu, and the costs were: Manufacturing: Fixed Variables Selling and administrative: Fixed Variables cu cu cu How much less would the company's net profit be " Dream" if she used direct costing instead of absorption costing? a.u.; b.e.; in cu; g.e What is the amount of profit of the Mechta company when using the absorption-costing system? a.u.; b.e.; in cu; y.e For the next year, the Salut company planned to sell units of product A, work-in-process inventories at the end of the period amounted to units of product A and work-in-process inventories at the beginning of the period amounted to 800 units of product A. All other inventories are equal to zero. How many finished units should be produced? a units; b units; in units; g units. The following information relates to questions 15 and 16: The company has decided to increase its output. Capital investments for the expansion of production of products N amount to a total of cu, which should be paid one-time to the contractor. During the first year, the equipment will be installed and there will be no production of N products. During the second year, the release and sale of product N is expected. At the end of the second year, the equipment will be sold at its residual value. Product data N for 1 piece (cu): Selling price 20 Variable costs 11 Fixed HP 4 Profit 5 At the same time, fixed overhead costs consist of depreciation - 1.50 c.u. and administrative overhead costs are 2.50 USD, and the rate of return is 12%. Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. 15
16 5.14 What is the net present value of this project? a.u.; b. (6,615) USD; V. (7,955) USD; g. (8,258) cu What is the accounting payback ratio based on the initial investment? A. 7.93%; b. 8.33%; V. 9.52%; 13.88% The Daimer company has the following basic production information for product P for the year: Basic materials 1.30 c.u. Basic labor 1.50 USD Variable production HP 0.20 USD Permanent production HP (distributed based on volume) $1.00 Selling price 5.00 USD The base volume of units of the product is R. Let us assume that selling and administrative expenses are constant and amount to c.u. per year, except for sales commissions amounting to 5% of sales income. What is the minimum price for a special order of units of Product P, assuming that the order does not affect Dimer's regular sales? a.u.; b.e.; in cu; g.e What is meant by opportunity costs? No. Costs that can be accurately and uniquely attributed to a specific target cost; b. Costs that are not affected by the decision; V. Avoidable expenses; d. Costs that measure the opportunity that is lost or sacrificed as a result of a choice. for sale Management Accounting 1. Mock exam. 16
17 5.18 The Solar company currently produces cardboard boxes, the production process of which is automated. The planned production volume is equal to units per month. The cost of basic materials is 0.3 USD. per unit. Manufacturing overhead costs are equal to c.u. per month. Manufacturing overhead is charged based on the number of units produced. What is the PNR distribution rate? A. 0.83 USD per unit; b. $1.00 per unit; V. 1.20 USD per unit; g. 1.50 USD per unit The forecast of the income statement for 2008 of the consulting firm “Good Advice” contains the following information: Revenue c.u. Total costs: Labor of specialists.e. Customer service c.u. Total costs c.u. Operating profit c.u. In a company, indirect costs are allocated based on labor costs. The Vkusnyashka restaurant chain placed an order with a consulting firm. To fulfill this order, the following volumes of work are planned for specialists: Category of specialists Hourly Planned rate, c.u. labor costs, hours Director Partner Companion Assistant What should be the order price for a restaurant chain if the ratio of net profit to total income is 10%? a.u.; b.e.; in cu; g.e. The following information relates to questions 21 and 22: The planned income statement for the production and sale of products in units of the Freema company for 2008 is as follows, in monetary units: Revenue Cost of sales () Gross profit Marketing research costs () Operating profit () The company's fixed production costs are 19.23% of revenue, and variable costs for marketing research are 4.000. per unit of goods. Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. 17
18 5.21 The company’s marginal income will be: a.u.; b.e.; in cu; g.e. By what number of units of production must the sales volume be increased for the company to earn c.u. arrived? a piece; b pcs.; in pcs.; g pcs Which of the losses in the production process are controllable? Standard Excessive a) yes yes b) yes no c) no yes d) no no 5.24 The company has planned the following costs for the 1st quarter of 2009, cu. month salary purchases general production payments income from expenses dividends sales January February March The cash balance as of February 1, 2009 will be c.u. Proceeds from the sale of products are paid as follows: 70% in the current month, 30% in the next month after the sale. All expenses are paid in the month in which they are incurred. What would be the net change in cash for February under this plan? for a.e.; b.e.; in cu; g.e.not sales Management Accounting 1. Trial exam. 18
19 5.25 Which statement is FALSE regarding by-products? A. These are products that appear during the production of basic products; b. The selling price in comparison with the cost of jointly produced products is the main criterion in their classification; V. By-products are critical to a company's business operations; d. By-products cannot be identified as separate products until a certain point in the production process. end of exam Management Accounting 1. Mock exam. 19
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting -1 Mock Exam (November 2014) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP/CIPA, CAP Certified trademarks
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting -1 Mock Exam (July 2015) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting trademarks
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting - 1 Mock Exam (JULY 2016) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, copyright holder of the trademarks CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting
CAP/CIPA library. "Tasks and solutions." Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. (November 2013 CAP/CIPA examination session) Material downloaded from the website www.capcipa.kz. For personal use.
CAP/CIPA library. "Tasks and solutions." Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. (March 2014 CAP/CIPA examination session) Material downloaded from kz.capcipa.org. For personal use.
Material downloaded from the website www.capcipa.kz.. For personal use. Copying and commercial distribution is prohibited. By CAP/CIPA Library. "Tasks and solutions." Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam.
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting -1 Mock Exam (July 2018) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, the copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting trademarks
CAP/CIPA library. "Tasks and solutions." Management Accounting 1. Mock Exam. The material was downloaded from the website www.capcipa.ua. For personal use. Copying and commercial distribution is prohibited.
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting -1 Mock Exam (November 2016) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting trademarks
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting -1 Mock Exam (November 2015) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, the copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting trademarks
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting -1 Mock Exam (March 2017) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, the copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting trademarks
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting -1 Mock Exam (November 2018) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, the copyright holder of the trademarks CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP/CIPA, CAP Certified
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting -1 Mock Exam (March 2015) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, the copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting trademarks
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting -1 Mock Exam (July 2017) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, the copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting trademarks
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting -1 Mock Exam (November 2017) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, the copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting trademarks
“Management Accounting 1” 2015 “Management Accounting 1” CONTENTS Lecture 1-6 3 Lecture 7-8 36 Lecture 10-13 67 Basic tests 91 Exams (without solutions) 111 Exams (with solutions) 170 Formulas 224 Problem 1 Part
CAP/CIPA library. "Tasks and solutions." Management Accounting 2. Mock Exam. (November 2013 CAP/CIPA examination session) Material downloaded from http://kz.capcipa.org. For personal use.
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting -1 Mock Exam (March 2016) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, the copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting trademarks
Test. Financial management Problem 1. The company produces musical instruments, including organs. The D-14 organ model is very promising and has a large potential market. Below is
Task 2.1. 1. Cost of materials used for the quarter Materials, January 1 $ 397,950 Purchases 1,225,330 Less: Materials, March 31 415,030 2. Manufacturing costs for the quarter $1,208,250 Direct
Qualification requirements for applicants for CAP qualification in the discipline “Management Accounting-1” Qualification requirements for participants in the exam “Management Accounting 1” For the course “Management Accounting”
TASKS FOR THE DISCIPLINE "ACCOUNTING AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING" Task 1. An industrial enterprise produces components (spare parts) necessary for assembling the main product. There is the following
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting 2 Mock Exam (November 2014) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting trademarks
1 Practical lesson on topic 9. Budgeting Questions for discussion: 1. What is the essence and purpose of the budgeting system? 2. Name the main functions of the budgeting system 3. What are
FEDERAL STATE EDUCATIONAL BUDGETARY INSTITUTION OF HIGHER EDUCATION FINANCIAL UNIVERSITY UNDER THE GOVERNMENT OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION (Penza branch) Department of Economics and Finance ACCOUNTING
EURASIAN COUNCIL OF CERTIFIED ACCOUNTANTS AND AUDITORS PROGRAM COURSE “MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING 1” Qualification requirements: participating in the program
1. General information about the discipline 1.1. Name of discipline: Production accounting 1..1 Discipline complexity 108 hours (3 ZE) of which full-time education: lectures 16 hours. laboratory classes 0 practical
Practical situation 1 Initial data (per unit of production) Price, rub. 500 Variable costs, rub. 300 Situation 1. The company produces 400 units of products per month. According to the marketing department, the increase
TOPIC 11. BUDGETING AND COST CONTROL 1. The essence of budgeting and its functions 2. The structure of the general budget 3. An example of drawing up an operating budget. 4. Financial budgets 1. ESSENCE OF BUDGETING
I/D 101 Qualification: Level 3 Diploma in Cost and Management Accounting (Qualification Accreditation Number: 500/2994/0) Examination: Cost and Management Accounting methods & analysis QUESTION PAPER DURATION:
PRACTICUM ON ACCOUNTING AND ANALYSIS Module 3. Fundamentals of management accounting Topic 2. The concept of costs and expenses of an enterprise, classification of costs Definition Costs the cost of resources used in the process
PRACTICUM ON ACCOUNTING AND ANALYSIS Module 3. Fundamentals of management accounting Topic 4. Cost calculation methods Classification of costing methods Costing methods By accounting objects order-by-process
Funds of valuation funds in the discipline “Management Accounting” Questions for the exam in the discipline 1. The essence and role of management accounting 2. The interaction of financial and management
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting - 2 Mock Exam (November 2017) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, copyright holder of the trademarks CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting
Management Accounting 1 Course Syllabus Qualification Requirements: Those participating in the CIPA Accounting Certification Program must demonstrate knowledge of the nature of management accounting.
Exam ID 101 Level 3 -Diploma in Cost and Management Accounting (Diploma in Management Accounting) (Qualification Accreditation Number 500/2994/0) MODULE NAME: Methods and analysis of cost and management accounting
Exam ID 121 QUESTION PAPER Qualification: Level 4 -Diploma in Financial Information for Managers (Qualification Accreditation Number 500/5035/7) Examination: Unit 2 Budgetary Control and Assessment of
B2.B.4 Budgeting Direction 38.03.01 “Economics” Profile: “Economics of enterprises and organizations of urban and housing and communal services” Qualification (degree) Bachelor Estimation Fund
ASSESSMENT FUND FOR INTERMEDIATE CERTIFICATION OF STUDENTS IN DISCIPLINE (MODULE) 1. Department General information 2. Direction of training 3. Discipline (module) 4. Number of stages of formation
CAP/CIPA library. "Tasks and solutions." Financial accounting 1. Assignment. November 2009 CIPAEN examination session. The material was downloaded from the website www.capcipa.ua. For personal use. Copying and commercial
Operational Level Exam P1 Operations Performance Management Option May 2012 Examiner Answers SECTION A: Answer to Question One 1.1 15,750 / 1.05 = 15,000 20,085 / 1.03 = 19,500 When used
APPLICATION for posting information in the educational portal of KEU Structure/Department: Accounting, analysis and audit Author(s): Omurkulova Gulmira Kadyrberdievna Title of material (work): Workshop on
Table 1. Project investments, rub. PROJECT INVESTMENT Q1 2017 Q2 2017 Q3 2017 TOTAL Buildings and structures Construction of infrastructure payment amount (including VAT) 30,000,000 30,000,000 40,000,000
TOPIC 6. “DIRECT COSTING” SYSTEM 1. Methods for calculating costs “Absorption costing” and “Direct costing”. 2. Financial reporting using the “Absorption Costing” and “Direct Costing” methods.
CAP/CIPA Library Management Accounting - 2 Mock Exam (July 2017) Material downloaded from the website of the CIPA Examination Network, the copyright holder of the CIPAEN, CIPA, CAP Certified Accounting trademarks
Problem solving: Financial management TASK. Draw up the following enterprise budgets for the second (ends June 30): Sales budget with a schedule for receiving money Production budget Acquisition budget
JSC "UNIVERSITY OF NARKHOZ" Scientific and pedagogical master's program Approved by the Minutes of the meeting of the department of "Business and Education" dated October 2016 by the head of the department "Dzhondelbaeva A.S." Doctor of Economics, Professor Full name Head of Department Examinations
COST DYNAMICS. BREAK-EVEN ANALYSIS 1. Cost dynamics 2. Separation of semi-variable cost elements 3. Break-even analysis of production 4. Graphical representation of CVP analysis 5. Margin of safety
APPLICATION for posting information in the educational portal of KEU Structure/Department: Accounting, analysis and audit Author(s): Berdibaeva K.T. Name of material (work): Management accounting Type (type) of material:
Tests in the discipline “Cost Management” 1. With an increase in production volume in the reporting period, how do fixed costs change: a) increase b) decrease c) remain unchanged d) no
TESTS IN THE DISCIPLINE “COST MANAGEMENT” 1. With an increase in the volume of output in the reporting period, how do fixed costs change: a) Increase b) Decrease c) Remain unchanged d) No
1 Practical lesson for topics 6 and 7. Direct costing system and management decision-making based on marginal profit analysis. Questions for discussion: 1. Name the fundamental difference between the system
IVASHKEVICH V.B. PRACTICE for independent work on management accounting Test tasks and exercises. Set of tasks A “Costs and results of the enterprise’s activities, calculation of parameters
AUDITORLAR CHAMBER OF KAZAKHSTAN REPUBLIC AUDITORLY CANDIDATES CERTIFICATIONS OF THE CHAMBER OF AUDITORS FOR AT TESTING OF CANDIDATES FOR AUDITORS
Tests 1,2, 3 and 4 on accounting. Procedure for selecting tasks The choice of option is based on the table below. The selection is based on the initial letter of the student's LAST NAME.
Assessment tools Assessment tools include ongoing progress monitoring tests and intermediate progress monitoring tests. 1. Tests for ongoing monitoring of TTKU progress 1. Use of a flexible budget
ALT-Invest Amount 6.1 Project description PROJECT PARAMETERS Project name: Installation of local modular boiler houses without HP Project start date 01/01/2016 Project life span 15 years Planning step year Duration
ALT-Invest Amount 6.1 Project description PROJECT PARAMETERS Project name: Installation of local modular boiler houses with HP Project start date 01/01/2016 Project life span 15 years Planning step year Duration
State educational budgetary institution of higher professional education "STATE UNIVERSITY - HIGH SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS" Higher School of Project Management
2. CONTROL QUESTIONS FOR THE DISCIPLINE “MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING AND ANALYSIS” 1. The purpose and essence of management accounting. 2. Requirements for management accounting and its information. 3. Principles of management
Using modeling in making daily decisions EGOR EGORUSHKIN Partner, director of the project office of the Here and Now Consulting Group Company Management There must be a Plan Deviation Accum.
BUSINESS PLAN LAYOUT The business plan is an integral part of the application of a small and medium-sized enterprise to receive financial support in the form of investments, preferential loans, interest-free
EXAMPLE OF ASSESSMENT TOOLS FOR EVALUATING PROFESSIONAL QUALIFICATIONS “CHIEF ACCOUNTANT WITH FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT FUNCTION” MOSCOW 2017 1. PASSPORT OF THE SET OF ASSESSMENT TOOLS 1.1. Application area Kit
Agreed by the certifying bodies (professional associations) - partners of CIPAEN PROGRAM AND CONTENT PLAN OF THE EXAMINATION “MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING 1” Contents 1. Summary of the program in the subject
Updated: 08/28/2019
How to open a CAP file?
There could be multiple reasons why you have problems opening CAP files on given system. What's important is that all common problems associated with files with the CAP extension, users can decide for themselves. The process is fast and does not require the participation of an IT specialist. The list below will guide you through the process of resolving your issue.
Step 1: Download and Install Netscout Sniffer
The most common reason for such problems is the lack of proper applications that supports CAP files installed on the system. This one is lightweight. Select Netscout Sniffer or one of the recommended programs (e.g. Wireshark, BoneLight, PacketView Pro) and download it from the appropriate source and install it on your system. At the top of the page there is a list of all programs grouped by supported operating systems. The safest way to download Netscout Sniffer is set - to do this, go to the developer's site () and download the software using the links provided.
Step 2: Check your Netscout Sniffer version and update if necessary
 If you already have it installed Netscout Sniffer on your systems and CAP files are still not opening properly, please check if you have the latest version of your software. Sometimes software developers introduce new formats to replace those already supported with new versions of their applications. This may be one of the reasons why CAP files are not compatible with Netscout Sniffer. All file formats that were handled perfectly by previous versions of this program should also be opened using Netscout Sniffer.
If you already have it installed Netscout Sniffer on your systems and CAP files are still not opening properly, please check if you have the latest version of your software. Sometimes software developers introduce new formats to replace those already supported with new versions of their applications. This may be one of the reasons why CAP files are not compatible with Netscout Sniffer. All file formats that were handled perfectly by previous versions of this program should also be opened using Netscout Sniffer.
Step 3: Assign Netscout Sniffer to CAP Files
After installing Netscout Sniffer (the most recent version), make sure that it is set as the default application for opening CAP files. The process for associating file formats with a default application may differ in detail depending on the platform, but the basic procedure is very similar.

Windows
- Right-clicking on CAP will open a menu from which you must select the option To open with
- Select Select another application→ More applications
- To end the process, select Find another app on this... and use File Explorer to select the Netscout Sniffer folder. Confirm Always use this application to open CAP files and clicking the OK button.

Procedure for changing the default program in MacOS
- By clicking right mouse button on the selected CAP file open the file menu and choose Information.
- Go to section To open with. If it's closed, click the title to access the available options.
- Select Netscout Sniffer and click Edit for everyone...
- If you completed the previous steps, a message should appear: This change will apply to all files with the CAP extension. Then click the Forward button to complete the process.
Step 4: Check CAP for errors
If you have followed the instructions from the previous steps and the problem is still not resolved, you should check the CAP file in question. Lack of access to a file can be due to various problems.

1. Check the CAP file for viruses or malware.
If it happens that CAP is infected with a virus, this may be the reason that prevents you from accessing it. Scan the CAP file and your computer for malware or viruses. If the CAP file is indeed infected, follow the instructions below.
2. Make sure the CAP file is complete and free of errors
If the CAP file was sent to you by someone else, ask that person to send you the file. It is possible that the file was copied by mistake and the data has lost its integrity, preventing access to the file. This may happen if the boot process file with CAP extension was interrupted and the file data was corrupted. Download the file again from the same source.
3. Check if the user logged in has administrator rights.
There is a possibility that this file can only be accessed by users with sufficient system privileges. Switch to an account with the necessary privileges and try opening the Packet Capture Format file again.
4. Make sure your device meets the requirements to open Netscout Sniffer
The operating systems may note enough free resources to run the application that support CAP files. Close all running programs and try opening the CAP file.
5. Check if you have the latest operating system and driver updates
The latest versions of programs and drivers may help you solve problems with Packet Capture Format files and ensure the security of your device and operating system. Outdated drivers or software may have caused the inability to use a peripheral device needed to handle CAP files.
CIPA program is the only comprehensive Russian-language program for international certification of professional accountants. The name of the program is an abbreviation of the English name of the CIPA certificate (Certified International Professional Accountant: Certified International Professional Accountant). Holders of CAP/CIPA certificates have the right to add the name of the certificate to their signature, which is in accordance with international practice. The CIPA program consists of three components: training, examinations and certification.
Qualification levels of the CIPA program
Candidates who successfully pass the required exams and fulfill additional qualification requirements are awarded the CAP and CIPA qualification levels with the issuance of the corresponding certificates:
- SAR(Certified Accounting Practitioner: Certified Accounting Practitioner, pronounced "cap"). The CAP is capable of maintaining the accounting system for the enterprise and preparing all the main reports, including tax returns.
- CIPA(Certified International Professional Accountant: Certified International Professional Accountant, pronounced "seepa"). CIPA is able to exercise professional judgment in financial management matters and participate in management decisions.
More detailed information about the exams, as well as the schedule of exam sessions for the current year, can be found in the "Exams" section.
Qualification requirements for obtaining CAP and CIPA certificates
| Requirement | CAP | CIPA |
|---|---|---|
1. Successful passing of exams:
|
75 75 75 — — — — — |
75 75 75 75 75 75 75 90 |
| 2. Higher professional education | — | required |
| 3. Confirmed work experience in the specialty | 1 year | 3 years |
| 4. Good reputation as a member of a professional organization | recommendation of an ECCBA member organization | |
| 5. Confirmation of basic qualifications in information technology | in accordance with the requirements of the professional association | exam |
Where can I get a certificate?
The CAP/CIPA certificate in.........has the right to be issued by 4 professional organizations members of ECCBA to their members, based on exams passed in the CIPA Examination Network. A list of these organizations can be found in the section of the site “
The content of the CIPA program is based on International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), as confirmed by the International Accounting Standards Committee Foundation (IASCF), the parent organization of the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), the developer of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). The IASCF representative also sits on the Board of Directors of the CIPA-EN examination network. The IASCF has granted the right to place its logo - a combination of octagons (Hexagon Device) - on CAP and CIPA certificates, as evidence of compliance of the content of the CIPA program with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
A candidate for a CAP level qualification must pass qualifying exams with a score of at least 75 points in the following disciplines:
Additional requirements for the candidate: professional work experience of at least one year, the necessary experience in working with computer programs, as well as membership in a professional organization - a member of ECCBA
